Understanding And Treating Different Types Of Acne
Understanding and treating different types of acne involves identifying the type and applying appropriate treatments. Effective acne management requires a tailored approach.
Acne can affect people of all ages and can significantly impact self-esteem. There are various types of acne, including whiteheads, blackheads, papules, pustules, nodules, and cysts.

Each type requires different treatments, ranging from over-the-counter products to prescription medications. Proper skincare routines and lifestyle changes are critical in managing acne.
Identifying the specific type of acne is crucial for selecting the most effective treatment plan. Consulting a dermatologist can provide personalized advice and treatment options. Effective acne management improves skin health and boosts confidence.
Types Of Acne
Acne can be frustrating and difficult to manage. Understanding the different types of acne is key to effective treatment.
Acne is not just pimples; it comes in various forms, each requiring a unique approach. Let’s explore the various acne types to understand and treat them better.
Non-inflammatory Acne

Non-inflammatory acne includes blackheads and whiteheads. These are the mildest forms of acne and do not cause swelling.
Blackheads are open comedones. They appear black due to the oxidation of melanin. They usually form on the nose, chin, and forehead.
- Caused by clogged hair follicles
- Not painful
- Appear black or dark brown
Whiteheads are closed comedones. They form under the skin and appear as small, white bumps. They are commonly found on the face, especially the cheeks.
- Caused by trapped oil and dead skin cells
- Not painful
- Appear white or flesh-colored
Effective treatments for non-inflammatory acne include:
- Regular cleansing with mild soap
- Topical retinoids
- Salicylic acid products
Inflammatory Acne
Inflammatory acne is more severe than non-inflammatory acne. It causes red, swollen, and painful lesions. The main types include papules, pustules, and nodules.
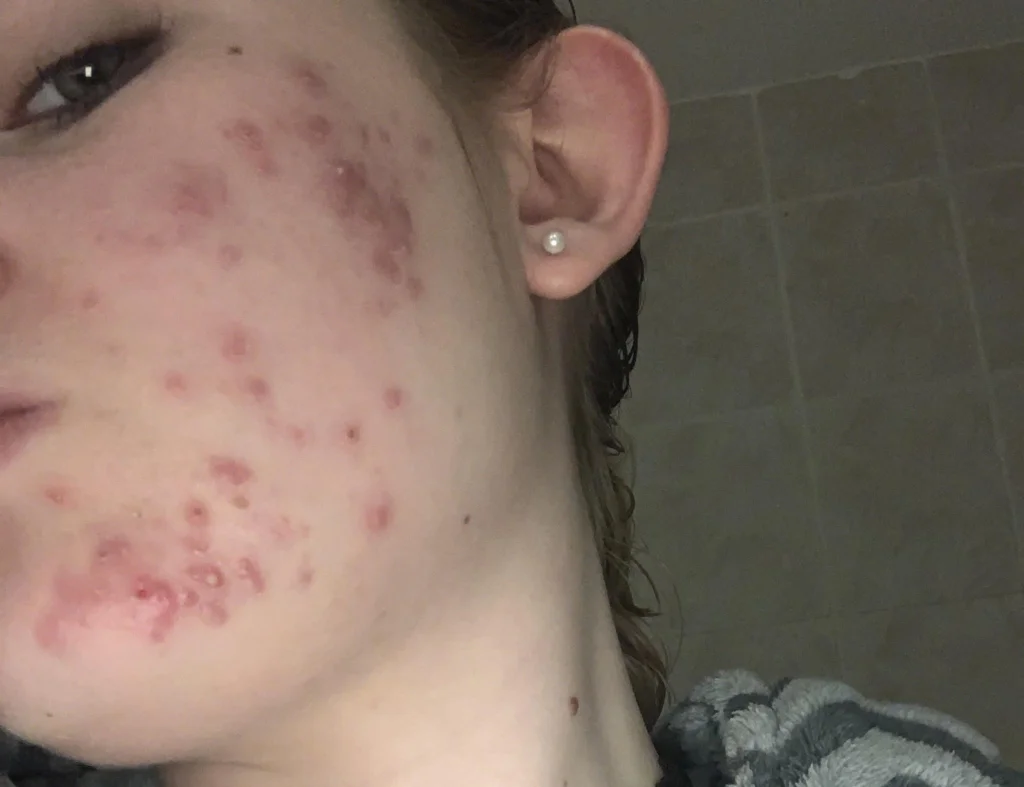
Papules are small, red, and raised bumps. They occur when the walls of the hair follicles break and become inflamed.
- Red and tender
- No visible pus
Pustules are similar to papules but contain pus. They appear as white or yellow bumps with a red base.
- Filled with pus
- Red and swollen
Nodules are large, hard, and painful lumps under the skin. They form deep within the skin and can cause scarring.
- Large and painful
- Deep under the skin
- Can cause scars
Treating inflammatory acne often requires the following:
- Prescription topical treatments
- Oral antibiotics
- Anti-inflammatory medications
Cystic Acne
Cystic acne is the most severe form of acne. It consists of large, painful cysts filled with pus, and it can lead to permanent scarring.

Cystic acne forms deep within the skin and is often caused by hormonal changes. The cysts are soft, large, and red or purple.
- Filled with pus
- Large and painful
- It can cause significant scarring
Effective treatments for cystic acne include:
- Oral antibiotics
- Isotretinoin (a powerful medication)
- Hormonal treatments (e.g., birth control pills)
- Corticosteroid injections
Professional medical advice is crucial for treating cystic acne. A dermatologist can provide tailored treatments to manage this severe condition.
Causes Of Acne
Understanding and treating different types of acne starts with identifying their causes. Acne can arise from various factors, each contributing uniquely to the skin’s condition. Knowing these causes can help in tailoring effective treatments.

Hormonal Imbalances
Hormonal changes can significantly impact the skin. Hormones like androgens can cause the sebaceous glands to enlarge and produce more sebum. This excess oil can clog pores, leading to acne.
- Teenagers often experience hormonal acne due to puberty.
- Women may see breakouts during menstrual cycles, pregnancy, or menopause.
- Conditions like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) can also trigger acne.
Managing hormonal acne might require specific treatments like:
- Oral contraceptives to regulate hormone levels.
- Anti-androgen drugs to reduce sebum production.
- Topical treatments that contain ingredients like benzoyl peroxide or salicylic acid.
Genetics
Genetics plays a crucial role in acne development. If your parents had acne, you’re also more likely to experience it. Genetic predisposition affects how your skin reacts to different triggers.
A study has shown that acne can run in families. Here’s a table summarizing genetic factors:
| Genetic Factor | Impact on Acne |
|---|---|
| Skin Type | Oily skin types are more prone to acne. |
| Sebum Production | High sebum production increases the risk. |
| Immune Response | Some individuals have a stronger inflammatory response. |
While you can’t change your genes, understanding your genetic predisposition can guide your treatment choices.
Diet And Lifestyle
What you eat and how you live affect your skin. Diet and lifestyle factors can contribute to acne in various ways.
- High-glycemic foods like white bread and sugary snacks can cause spikes in blood sugar levels, leading to breakouts.
- Dairy products may increase the risk of acne in some people.
- Stress can trigger hormonal changes, leading to more oil production.
Adopting a balanced diet and healthy lifestyle can reduce acne occurrences. Here are some tips:
- Eat more fruits and vegetables to provide essential nutrients.
- Reduce intake of processed foods to avoid spikes in blood sugar.
- Practice stress-reducing activities like yoga or meditation.
Environmental Factors
The environment around you can also influence acne. Pollution, humidity, and exposure to certain chemicals can all contribute to skin issues.
- Pollutants can clog pores and cause inflammation.
- High humidity levels can increase oil production, leading to breakouts.
- Exposure to harsh chemicals in skincare products can irritate the skin.
To mitigate environmental impacts, consider the following:
- Use non-comedogenic skincare products that don’t clog pores.
- Cleanse your face regularly to remove pollutants and excess oil.
- Use a humidifier to maintain optimal humidity levels indoors.
Diagnosis Of Acne
Acne is a common skin condition that affects people of all ages. Understanding and treating different types of acne requires accurate diagnosis, which involves several steps.
Each step helps to identify the type and severity of acne, enabling effective treatment plans. This section will explore the physical examination, medical history, and laboratory tests involved in diagnosing acne.
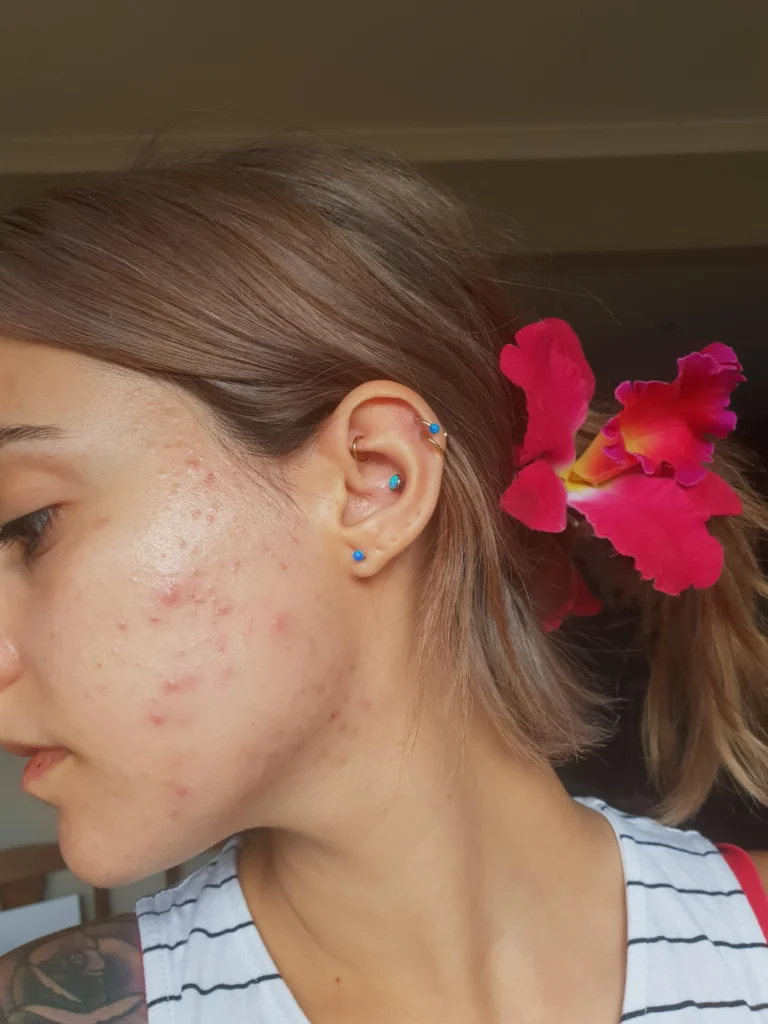
Physical Examination
The physical examination is the first step in diagnosing acne. A dermatologist examines your skin to identify the type and severity of acne. The doctor looks for different types of acne lesions. These include:
- Whiteheads: Small, white bumps under the skin.
- Blackheads: Small, black, or dark-colored bumps.
- Papules: Small, red, raised bumps.
- Pustules: Red bumps with white or yellow pus.
- Nodules: Large, painful, solid lumps under the skin.
- Cysts: Painful, pus-filled lumps under the skin.
The dermatologist also checks the distribution of acne on your face, chest, back, and shoulders. This helps in understanding the extent of the condition. The severity of acne is often categorized as mild, moderate, or severe.
This categorization guides the treatment plan. In some cases, the doctor might use a dermatoscope. This tool magnifies the skin and provides a clearer view of the lesions.
Medical History
Taking a detailed medical history is crucial in diagnosing acne. The doctor asks about your personal and family history of acne. This helps identify genetic factors contributing to the condition. Important questions include:
- Onset: When did you first notice acne?
- Duration: How long have you had acne?
- Previous Treatments: Have you tried any treatments before? Were they effective?
- Medications: Are you currently taking any medications? Some drugs can cause or worsen acne.
- Hormonal Changes: Have you noticed any changes in your acne related to your menstrual cycle, pregnancy, or menopause?
- Lifestyle: Do you have any lifestyle factors that might affect acne, like diet or stress?
The doctor may also ask about your skincare routine, including the products you use and how often you use them. A thorough medical history provides insights into potential triggers and helps tailor a treatment plan.
Laboratory Tests
In some cases, laboratory tests are necessary to diagnose acne. These tests help to rule out other conditions and identify underlying causes. Common tests include:
- Hormone Levels: Blood tests to check for hormonal imbalances. Hormones like androgens can contribute to acne.
- Skin Swab: A sample is taken from the skin to check for bacterial infections. This test identifies the presence of acne-causing bacteria.
- Allergy Tests: Tests to identify any allergies that might be causing or worsening acne.
A hormonal panel may be conducted for women. This includes tests for testosterone, estrogen, and other hormones.
Elevated levels of these hormones can lead to acne. Another common test is the blood sugar test. High blood sugar levels can worsen acne, particularly in individuals with insulin resistance.
Doctors can accurately diagnose acne by combining the results of physical examinations, medical history, and laboratory tests. This comprehensive approach ensures effective and personalized treatment plans.
Treatment Options
Acne affects millions of people worldwide, and treating it can be challenging. Understanding the different types of acne and their treatment options is crucial. Various methods exist, from topical creams to home remedies, to manage and reduce acne effectively.

Let’s explore these treatment options.
Topical Medications
Topical medications are the first line of defense against acne. They are applied directly to the skin and can help reduce inflammation, unclog pores, and kill bacteria. These medications come in various forms, such as creams, gels, and lotions.
Common topical medications include:
- Benzoyl Peroxide: Helps kill acne-causing bacteria and reduce inflammation.
- Salicylic Acid: Unclogs pores and prevents future breakouts.
- Retinoids: Derived from vitamin A, they promote cell turnover and prevent clogged pores.
- Antibiotics: Reduce bacteria and inflammation on the skin.
It’s essential to use these medications as directed by a healthcare provider. Overuse or improper application can lead to skin irritation or dryness.
Oral Medications
Oral medications might be necessary for moderate to severe acne. These medications work from within the body to address the root causes of acne. They are typically prescribed when topical treatments alone are not sufficient.
Common oral medications include:
- Antibiotics: Help reduce bacteria and inflammation.
- Oral Contraceptives: Regulate hormones that can cause acne.
- Isotretinoin: A powerful drug that reduces oil production and inflammation.
- Spironolactone: Helps reduce hormonal acne in women.
These medications should be taken under the guidance of a healthcare provider due to potential side effects.
Procedures
Several procedures can help treat acne and improve skin appearance. These treatments are usually performed by dermatologists and can provide significant results.
Common procedures include:
- Chemical Peels: Use acids to exfoliate the skin and remove dead cells.
- Laser Therapy: Targets bacteria and reduces oil production.
- Drainage and Extraction: Removes large cysts and reduces pain.
- Microneedling: Stimulates collagen production and reduces acne scars.
These procedures can be costly and may require multiple sessions for optimal results.
Home Remedies
Home remedies can be effective for mild acne and are a cost-effective option. They use natural ingredients that are gentle on the skin.

Popular home remedies include:
- Tea Tree Oil: Has antibacterial properties that reduce acne.
- Aloe Vera: Soothes and heals inflamed skin.
- Honey: Natural antibacterial agent that helps heal acne.
- Green Tea: Reduces oil production and inflammation.
These remedies can be easily incorporated into a daily skincare routine but should be used consistently for best results.
Prevention Of Acne
Understanding and treating different types of acne can be challenging. Yet, prevention plays a crucial role in managing acne effectively. By adopting healthy habits, you can significantly reduce the occurrence of acne. Here are some essential tips for preventing acne.

Maintain A Healthy Diet
Diet plays a vital role in skin health. Certain foods can trigger acne, while others can help prevent it. To keep your skin clear, follow these dietary guidelines:
- Eat more fruits and vegetables: They are rich in vitamins and antioxidants that promote healthy skin.
- Reduce sugar intake: High sugar levels can lead to acne breakouts.
- Choose whole grains: They have a low glycemic index, which helps control blood sugar levels.
- Incorporate healthy fats: Omega-3 fatty acids found in fish and flaxseeds can reduce inflammation and acne.
Here is a simple table to help you choose acne-friendly foods:
| Foods to Eat | Foods to Avoid |
|---|---|
| Leafy greens, berries, nuts | Sugary snacks, white bread, soda |
| Whole grains, fish, seeds | Fried foods, dairy products, chocolate |
Regular Exercise
Exercise is good not only for your body but also for your skin. Regular physical activity can help in preventing acne by:
- Improving blood circulation: Better blood flow helps to nourish skin cells and keep them healthy.
- Reducing stress: Exercise helps lower stress levels, preventing stress-induced acne.
- Regulating hormones: Physical activity can balance hormones, which is beneficial for preventing hormonal acne.
To make the most out of your workout:
- Choose activities you enjoy, like swimming, cycling, or dancing.
- Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate exercise daily.
- Always shower after workouts to remove sweat and bacteria from your skin.
Good Hygiene Practices
Maintaining good hygiene is essential for preventing acne. Here are some practices to follow:
- Wash your face twice daily: Use a gentle cleanser to remove dirt, oil, and makeup.
- Keep your hands off your face: Touching your face can transfer bacteria and oil, causing breakouts.
- Change pillowcases regularly: Pillowcases can harbor oil, dirt, and bacteria contributing to acne.
- Clean your phone screen: Phones collect bacteria that can transfer to your face.
Here’s a quick checklist for good hygiene:
| Action | Frequency |
|---|---|
| Face washing | Twice daily |
| Pillowcase change | Weekly |
| Phone screen cleaning | Daily |
Avoiding Certain Products
Some skincare and hair products can cause acne. To prevent breakouts, avoid products with the following ingredients:
- Comedogenic ingredients: These clog pores and lead to acne. Look for “non-comedogenic” labels.
- Heavy oils: Oils like coconut oil can be too thick and clog pores.
- Fragrances and dyes: These can irritate the skin and cause breakouts.
To choose the right products:
- Read labels carefully and avoid comedogenic ingredients.
- Opt for products labeled as “oil-free” or “non-comedogenic.”
- Test new products on a small skin patch before full application.
By following these tips, you can significantly reduce the occurrence of acne and enjoy clearer, healthier skin.
Complications Of Acne
Acne is not just a skin issue. It can lead to various complications that affect one’s mental and physical health. Understanding these complications helps in effective treatment and management.
In this section, we will dive into the complications of acne, including psychological effects, scarring, and hyperpigmentation.
Psychological Effects
Acne affects more than just your skin. It can lead to significant psychological distress. Many individuals with acne experience:
- Low self-esteem: Acne can make people feel unattractive.
- Social anxiety: Fear of being judged can lead to avoidance of social situations.
- Depression: Persistent acne can contribute to feelings of sadness and hopelessness.
Studies show that acne sufferers are more likely to experience mental health issues. A survey by the American Academy of Dermatology found:
| Psychological Issue | Percentage of Acne Sufferers |
|---|---|
| Low self-esteem | 85% |
| Social anxiety | 70% |
| Depression | 50% |
Addressing the psychological effects of acne is crucial. Mental health support, counseling, and dermatological treatments can help. Boosting confidence and improving mental well-being should be part of acne management.
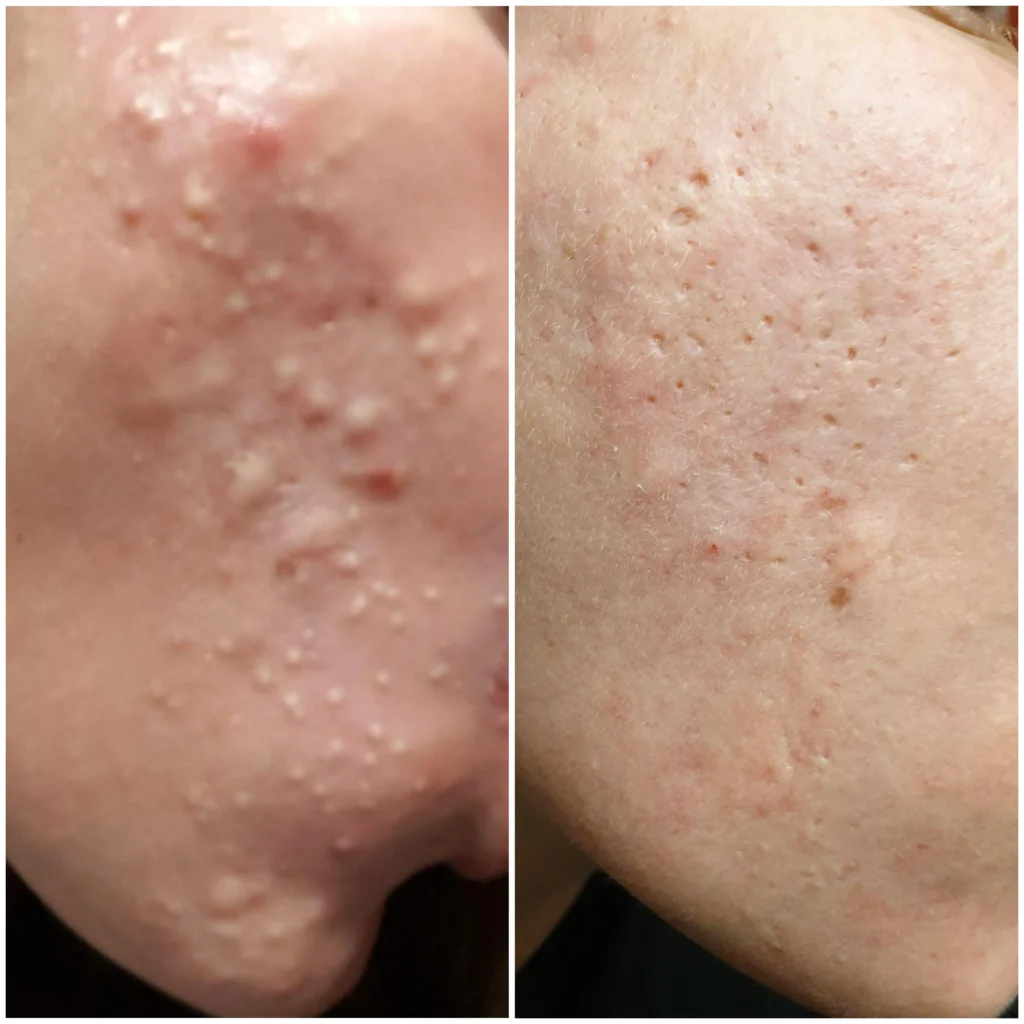
Scarring
Scarring is a common complication of acne. It occurs when severe acne damages the skin. There are several types of acne scars:
- Ice pick scars: Deep, narrow scars that look like pinpricks.
- Boxcar scars: Broad, rectangular depressions with sharp edges.
- Rolling scars: Wavy depressions in the skin.
Scars can be permanent and affect one’s appearance. Treatment options for acne scars include:
- Laser therapy: Reduces the appearance of scars by resurfacing the skin.
- Chemical peels: Removes the top layer of skin to reduce scar depth.
- Microneedling: Promotes collagen production to heal scars.
Early treatment of acne can prevent scarring. Dermatologists can recommend the best treatment based on scar type. Consistent skin care routines also help minimize scarring.
Hyperpigmentation
Hyperpigmentation is another common complication of acne. It occurs when the skin produces excess melanin in response to inflammation, resulting in dark spots or patches on the skin.
Types of hyperpigmentation include:
- Post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH): Dark spots that appear after acne heals.
- Melasma: Brown or gray-brown patches, often triggered by hormonal changes.
Hyperpigmentation does not cause physical harm but affects appearance.
Treatments for hyperpigmentation include:
- Topical treatments: Creams containing ingredients like hydroquinone, retinoids, or vitamin C.
- Chemical peels: Helps to exfoliate and lighten dark spots.
- Laser therapy: Targets pigmentation to even out skin tone.
Preventing hyperpigmentation involves using sunscreen daily. Sunscreen protects the skin from UV rays that can worsen dark spots. Consistent use of acne treatments can also reduce the risk of hyperpigmentation.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Do I Identify What Type Of Acne I Have?
Identify the type of acne by examining the size, color, and pain level. Consult a dermatologist for an accurate diagnosis.
How Do I Know What Acne Treatment To Use?
Consult a dermatologist for personalized advice. Identify your skin type and acne severity. Consider products with benzoyl peroxide, salicylic acid, or retinoids. Always patch-test new treatments.
Which Type Of Acne Is Most Difficult To Treat?
Nodulocystic acne is the most difficult to treat. It involves large, painful nodules and cysts deep under the skin. Treatment often requires prescription medication or professional procedures.
What Are The 4 Levels Of Acne?
The four levels of acne are mild, moderate, severe, and cystic. Mild acne includes small pimples and blackheads. Moderate acne involves more inflamed pimples. Severe acne features numerous painful, inflamed lesions. Cystic acne includes deep, painful cysts and nodules.
Conclusion
Understanding and treating different types of acne is crucial for clear skin. Choose the right treatment based on your acne type. Consult a dermatologist for personalized advice.
Proper skincare can significantly improve your skin’s health. Stay consistent with your routine and monitor your progress for the best results.






